Diesel Particulate Filters (DPFs) are critical components in modern diesel engines designed to reduce harmful emissions and comply with environmental regulations. In this article, we’ll delve into the purpose and functioning of DPFs, discuss their maintenance requirements, and explore their importance in the context of eco-friendliness and diesel engine performance.
What is a DPF?
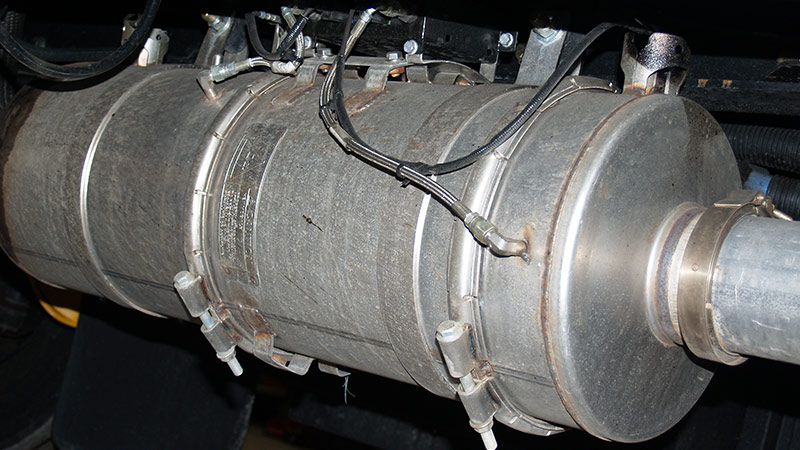
A DPF filter is an exhaust system component designed to capture and reduce particulate emissions generated by diesel engines. These emissions, often referred to as soot or particulate matter, can be harmful to both human health and the environment. DPFs are instrumental in trapping and subsequently burning off these particulates, making diesel engines more environmentally friendly.
How Does a DPF Work?
DPFs function through a process called regeneration. Here’s a simplified overview of how it works:
- Particulate Collection: As exhaust gases flow through the DPF, particulate matter is captured and trapped within the filter’s porous walls.
- Accumulation: Over time, the captured soot and particles accumulate within the filter, reducing its efficiency and potentially causing increased backpressure on the engine.
- Regeneration: To prevent excessive buildup and maintain optimal performance, DPFs undergo regeneration. This process involves raising the exhaust gas temperature to a point where the trapped soot and particles burn off, leaving behind ash.
- Ash Removal: While soot is burned away during regeneration, ash remains as a non-combustible residue. Periodically, DPFs must undergo ash removal through maintenance or replacement to maintain efficiency.
Importance of DPFs
1. Emission Reduction: DPFs are a vital tool in reducing harmful particulate emissions, helping diesel engines meet stringent environmental standards and regulations. They play a crucial role in decreasing air pollution and improving air quality.
2. Compliance: Many regions and countries have established strict emission standards for diesel vehicles. DPFs are essential for diesel engine compliance with these regulations, avoiding fines and penalties for non-compliance.
3. Engine Performance: Properly functioning DPFs contribute to optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. Clogged or inefficient DPFs can lead to reduced power, lower fuel economy, and increased maintenance costs.
DPF Maintenance
Maintaining a DPF is essential to ensure it operates efficiently and continues to reduce emissions effectively. Here are some key maintenance considerations:
- Regular Inspections: Regularly inspect the DPF for signs of excessive soot buildup, cracks, or damage. Address any issues promptly.
- Regeneration: Allow the DPF to undergo regeneration as needed. Modern diesel vehicles are equipped with systems that initiate regeneration automatically when required.
- Proper Fuel and Oil: Use high-quality diesel fuel and engine oil, as low-quality products can contribute to increased soot production and DPF clogging.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule for your specific vehicle, including DPF maintenance and cleaning.
- Professional Maintenance: Consider professional DPF cleaning services or replacements when necessary to ensure optimal performance.
Diesel Particulate Filters (DPFs) are indispensable components in diesel engines, serving to reduce harmful emissions, improve air quality, and ensure compliance with environmental regulations. Proper maintenance and understanding of DPF operation are essential for diesel vehicle owners to enjoy optimal engine performance while minimizing their environmental impact. By following manufacturer guidelines and staying proactive in DPF maintenance, diesel engine operators can contribute to a cleaner, healthier environment while reaping the benefits of efficient and reliable vehicles.